- Author admin caroline@plants-knowledge.com.
- Public 2023-12-17 03:39.
- Last modified 2025-06-01 06:48.
Severely itchy bite marks on the skin can be an indication of mites. Various strains of mites live parasitic lives, which we humans also use as a source of food. While the classic house dust mite waits for us in bed, wood mites lurk in the tall grass of the garden. Arachnid bites are similar to mosquito bites, but cause different symptoms and illnesses. In order to take the right measures against mites, it is important to find the cause of the itchy and inflamed skin areas.
What are mites
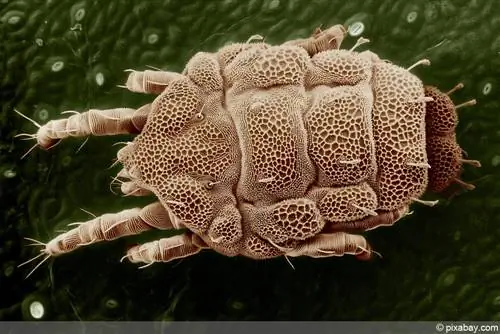
Just like ticks, many mites are parasitic arachnids that can trigger and transmit allergies and diseases. With the naked eye it is difficult to detect and identify the animals, which are only a maximum of 0.5 mm in size. The bites of the pests are noticeable and painful. People and animals are affected equally. Mites belong to the most species-rich family group of arachnids. Around 50,000 different species of small arthropods are known worldwide, although only a small fraction of them can be dangerous to humans and animals.
Some species of mites have specialized in four-legged animals. The parasites feed on the body secretions of the host animals, which can have unpleasant consequences for them. Some types of mites multiply on the infected animal. Mange mites, for example, lay their eggs under the skin of dogs and cats. The larvae hatch after a few days and the cycle of parasitic arachnids begins again. Scabies and house dust mites can cause significant complications in humans. Examples of diseases transmitted by mites include:
- Scabies
- Spotted Fever
- Tularemia
- Lyme disease
- Rickettsipox
habitat
As different as the lifestyles of the individual mite species are, their natural habitat is just as diverse. However, just over half of all mite species that occur colonize the soil and in this way contribute productively to the formation of humus. Parasitic arachnids, on the other hand, are often found on their host. While some species spend their entire lives there and are only transmitted through physical contact, other mites drop and lurk in the tall grass and dense bushes for new victims. Ticks, for example, are known for this way of life. These blood-sucking ectoparasites are not picky and do not stop at large and small vertebrates, including us humans.
Digging mites go one step further. These parasites are not content with colonizing the upper layer of skin of mammals. The damaged mites create boreholes, which cause severe itching. The larvae of these pests cause the dreaded skin disease scabies. This clinical picture in animals is colloquially called mange. The disease is highly contagious and must be treated immediately.
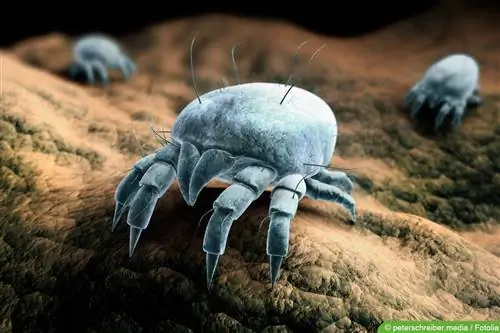
House dust mites could be viewed as “cultural followers”. The small parasites are one of the best-known species of mites that share their habitat with humans. The arachnids find a rich supply of food in mattresses and bed linen in the form of fungi that grow on skin scales. The mite droppings trigger asthma and the dreaded house dust mite allergy. In contrast to other types of mites, house dust mites cannot be completely eliminated despite intensive efforts. The pest population and the associated he alth risks can be reduced to a minimum.
Wood mites - stubborn pests
House dust mites and the like are not the only arachnids that are dangerous to us humans. Wood mites, which are also known as autumn grass mites, hay louses or harvest mites, belong to the group of walking mites. The common names of these arachnids indicate their natural habitat: The majority of these parasitic insects live predominantly on meadow plants, shrubs and bushes. Even in your own garden you are not protected from Neotrombicula autumnalis, the Latin name for these pests. A dry, sunny climate favors the reproduction rate of mites.
The little crawlers are not equally represented everywhere. In some regions of Germany it is almost a miracle to see them. Other areas, such as Bavaria and the Rhine region, are among the pests' preferred settlement areas. Once the small arachnids are present, it is difficult to get rid of them.
With their mouthparts, the larvae of the walking mites are able to penetrate human skin and absorb lymphatic fluid unnoticed. When bitten, an enzyme is injected which causes unpleasant itching. The rash can last for several days and take extreme forms. Pathogens can also be transmitted to the host while the pests are feeding.
While it is difficult to recognize the larvae of Neotrombicula autumnalis with their 0.3 mm, you can easily identify the adults with a trick:
- Lay out dark cardboard or black fabric on the grass
- This measure is optimal during lunchtime
- The red arachnids prefer the warm material
- The mite population reaches its peak in mid or late summer
If the wood or harvest mites are present in large numbers in the garden, this can be seen after a short time by looking at the box or fabric. It is rare for a location to be uniformly affected by a grass mite infestation. The small arachnids usually settle in a small area of around half a square meter. If you suspect a population of wood mites in your garden, you should carry out the “mite sample” in different places at the same time.
Detecting mite bites on people
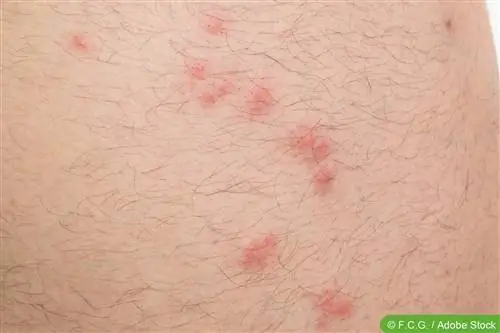
Mite bites are painful and can cause long-lasting skin irritations and eczema. By carefully observing the external appearance of the stings, you can easily identify the species of arachnid responsible for them. In this way it is possible to take effective measures against the harmful insects.
- Swelling, redness and itching occur around the bite sites
- The “stitches” are regionally limited and are usually close together
- Mite bites are easily confused with insect bites
- The bites of burrowing mites are associated with pain
- Tubular, approximately pin-sized vesicles are characteristic of burrowing mites
- The scabies-like symptoms only appear after a few weeks
- A scale-like skin appearance combined with severe redness is an indication of predatory mites
- Slight fever can occur in sensitive people after a mite bite

Neotrombicula autumnalis are picky about their food intake. The small arachnids prefer a warm, moist, protected place. For this reason, a large number of these bites occur on the edges of tight-fitting textiles, such as socks, underwear and the waistband of trousers. The armpits are also occasionally affected. The itching increases continuously in the first 2 to 3 days, spots and swelling only appear after 5 to 36 hours. If the bite sites are left untreated, the itching and redness can last for several weeks.
Tip:
Cover your legs and arms while gardening. In addition, work gloves not only protect against grass mites, but also against thorns and toxic plant juices.
First aid measures for bites
Only a fraction of parasitic mites are active vectors of disease. However, when the arachnids penetrate human skin with their biting tools, they create a potential entry portal for many skin diseases and infections. The severe itching also makes you constantly scratch the affected areas. This can cause further injuries, including open wounds. Bacteria invade, which in the worst case can lead to blood poisoning. It makes sense to treat mite bites in good time.
An infection with burrowing mites is not something that should be taken lightly and can be treated yourself with home remedies. Just a few centuries ago, countless people died of scabies. Fortunately, thanks to modern research and effective medicine, these consequences are a thing of the past. However, scabies is still a current issue. The earlier the symptoms and the infestation are treated, the better for the affected person and those around them. Just a handshake is enough to become infected with the dangerous burrowing mites. The treatment itself is carried out by a qualified doctor.
In contrast to scabies mites, wood mites only visit their “host” for a short time. Once the itching occurs, it is usually too late. The perpetrators left the crime scene hours ago. You should stay away from the bites. Because these tear open quickly and can leave small scars. The following tips have proven to be effective:
- Rub affected areas with lemon juice
- Apply high-percentage alcohol to the skin surface using cotton wool
- The juice of an onion can also provide relief from itching
- Remedies for scabies do not help with grass mite bites
Alcohol compresses, ointments containing cortisone and antihistamines from the pharmacy relieve itching and allow inflammation to subside more quickly. For medical products, it makes sense to read the package insert carefully. Many medications, especially the effective antihistamine, cause severe tiredness.
Preventive measures
There is no effective repellent against mites. The arachnids develop a natural resistance to many chemical products within a short period of time, which is passed on to the next generations. While you can keep house dust mites at bay with cleanliness and regular bed linen changes, you can only reduce the risk of a burrowing mite infestation to a minimum by avoiding contact with affected people. It is similar with wood mites. The following defensive measures have also proven effective against the animals:
- Mow grass regularly in the garden, this reduces the grass mite population
- Change clothes and shower when staying in endangered areas
- Check the fur of free-roaming dogs and cats regularly for pests
- Apply neem oil if there is a mite population on stone
It is not uncommon for Neotrombicula autumnalis to be advised to apply hot water or vinegar and oil. However, these products have no place in the garden because they can have a significant impact on the flora and fauna. The same principle applies to insecticides. Wood mites love thick moss cushions in the lawn. Prevent severe infestation and scarify the grass in spring. With this measure you can renovate the green area and make life difficult for the small arachnids.
Tip:
You can temporarily keep wood mites at bay using special sprays. Effective products are available in drugstores and pharmacies.
If neither humans nor larger mammals are present, the red parasites make do with mice. A large population of these rodents can cause a high mite infestation in the garden. Use the following tips to make your garden unattractive to mice:
- Dig up and turn compost heaps regularly
- Remove potential food sources, such as fallen fruit, immediately
- Natural predators, such as hedgehogs and birds, can effectively contribute to decimation
- The useful animals feel at home in a natural garden with many opportunities to retreat
Wood mites in the house
The little red arachnids are not only native to the wild. Under certain circumstances they can make life difficult for us in the house. In bed and on the sofa we are exposed to pests without any protection. Similar to the garden, it is itchy and discolored areas of skin that alert us to the presence of grass mites in the house. Observe the suspicious areas closely. You need to act quickly as soon as you have located the grass mites.
- Put delicate textiles and cuddly toys in the freezer for approximately 24 hours
- Clean bed linen and towels in the washing machine at at least 60° C
- Suck the area with a special dust mite vacuum cleaner
- Use mite-proof sheets
The parasites are stubborn. It cannot be ruled out that a one-time cleaning campaign will have little effect. For this reason, it makes sense to repeat the above measures daily. Steam cleaners are suitable for deep pore cleaning of beds. If necessary, you can rent these along with the appropriate cleaning agent from retailers. Be thorough and allow the mattresses to dry thoroughly. In addition to wood mites, you can also eliminate house dust mites in this way.
Conclusion
Mites are annoying; the bite of the arachnids, which are only a few millimeters long, can have serious consequences. In order to take the right countermeasures, it makes sense to classify the type of mite. For example, remedies against digging mites are ineffective against house dust and grass mites. The red pests can cause severe itching. However, the small parasites do not pose a danger to humans. You can combat the sequelae of bites quickly and effectively with home remedies and over-the-counter products from the pharmacy.