- Author admin caroline@plants-knowledge.com.
- Public 2023-12-17 03:39.
- Last modified 2025-06-01 06:48.
Tomatoes not only impress with their intense taste, but also with their high nutritional value! The red fruits are real vitamin bombs and also provide a lot of minerals. This article provides an overview of the most important ingredients as well as useful information about the nutritional value!
Nutritional values
Tomatoes are not only extremely tasty, but also very he althy. Because they consist of over 90 percent water and contain only a few calories. The fructose contained in many types of tomatoes provides a pleasant sweetness, but it hardly weighs on the scales. For this reason, the red fruits are a he althy snack between meals and can also be eaten safely while on a diet.
Nutritional values per 100 grams
| Calorie | 13 - 19 g |
| Fat | 0, 2 - 0, 7 g |
| Protein | 0, 7g |
| Carbohydrates | 1, 9 - 4, 0 g |
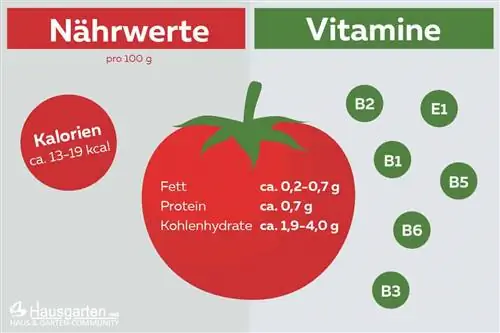
Vitamins
The red fruits are rightly considered a real vitamin bomb because they contain a variety of different vitamins. Above all, vitamin C should be mentioned, the content of which is around 25 milligrams per 100 grams of tomatoes. A medium-sized tomato can therefore provide around 30 percent of the recommended daily dose of vitamin C. However, it should be noted that most of the vitamin C is in the peel. The tomato peel contains around three times as much vitamin C as the pulp. The tomato also provides the following vitamins:
- Vitamin B1, B2, B6 and E1
- Niacin (B3)
- Pantothenic acid (B5)
Minerals
Tomatoes not only provide valuable vitamins, but also a variety of minerals. The potassium content is particularly worth mentioning at around 297 milligrams per 100 grams. This is an essential mineral that is involved, among other things, in protein production, the utilization of carbohydrates, the conduction of nerve impulses and muscle contraction. In addition to potassium, tomatoes also contain the following minerals:
Minerals per 100 grams
| Iron | 0, 5 mg |
| calcium | 10 mg |
| Sodium | 250 mg |
| Magnesium | 14 mg |
| Phosphorus | 22 mg |

Did you know:
After the flu, many people suffer from a potassium deficiency, which can be compensated for by regular consumption of tomatoes.
Lycopene
Most tomato varieties have a typical red color, which can be traced back to the substance “lycopene”. Lycopene is not only responsible for the red color, as the secondary plant substance is also said to have numerous he alth effects. Lycopene is said to be able to inhibit the growth of cancer cells and lower systolic blood pressure, among other things. Lycopene is found in raw fruits at an amount of around 9.3 milligrams per 100 grams. The lycopene content is even higher in processed products because the substance is released particularly well in high heat.
Lycopene per 100 grams
| Tomato juice | 10, 8 mg |
| Tomato puree | 16, 7 mg |
| Ketchup | 17, 2 mg |
| Tomato Sauce | 18, 8 mg |
| Tomato paste | 55, 5 mg |
Histamine and Solanine
Tomato fruits not only contain numerous he alth-promoting substances, but also two that should always be enjoyed with caution. On the one hand, this includes histamine, which is contained in around 20 milligrams in around one kilogram of tomatoes. The amount is relatively small, but people with histamine intolerance react to even the smallest amounts of histamine, which is why they should not eat the red fruits. Green, unripe specimens should generally not be consumed because they contain a particularly high amount of solanine, which can be toxic. However, the solanine content decreases enormously as ripening progresses, so there is basically no danger with ripe fruits.






