- Author admin caroline@plants-knowledge.com.
- Public 2023-12-17 03:39.
- Last modified 2025-01-24 12:45.
If you observe caterpillars in raised beds or gardens, you should act quickly. If the pests are not discovered in time, the population will expand significantly within a short period of time. To combat the plague, home remedies can be used as a deterrent or as an obstacle. Targeted prevention of the spread of pests is better than control.
Low pest spread
If the infestation is not yet advanced, you can collect and dispose of the pests at dusk. This measure is carried out until the number of cutworms has visibly reduced. Regular follow-up inspections during the summer months are necessary in order to eliminate pests that appear later.
Attract
Cutworms are nocturnal and retreat into self-dug holes in the ground during the day. This way of life makes it difficult to collect the pests. They can be specifically lured out of their hiding places. A mixture of bran, sugar and water is suitable as bait.
- 200 grams of oat bran
- three tablespoons of sugar
- double the amount of water
- some ground bitterwood
Quenching
Caterpillars are sensitive to the smell of some substances. Essential oils and intense aromas keep the annoying creatures away from raised beds and gardens.
Spices

Dried culinary herbs contain essential oils that have a repellent effect on cutworms. Regularly mix a teaspoon of thyme or sage into the water and let the extract stand for a while before administering. Young plants can be watered with the tea. Garlic has similar effects to intensely fragrant spices. Sprinkle the powder on the soil or plant garlic plants in the bed. A cut garlic clove in the substrate gives off an intense scent and keeps pests away.
Tip:
In mixed crops there is less risk of pest spread. Plant tomato plants in the garden and raised beds because their aroma deters caterpillars.
Tobacco
The smell of cigarette butts has a deterrent effect on the offspring of the voracious butterflies. Fresh tobacco can also be spread on the substrate as a preventative measure. It should be used carefully as tobacco contains a highly effective neurotoxin. It also harms other organisms and must not enter the soil.
Tip:
The roasted aromas of the coffee powder have a deterrent effect on many pests. Sprinkle coffee grounds regularly on the substrate as an alternative to tobacco.
Barriers
Some home remedies have proven to be effective obstacles that pests find difficult to overcome. They are suitable as gentle alternatives to pesticides.
Eggshells

Small ground eggshells are distributed around the shoot base of the plants as a natural barrier. The pests cannot overcome the sharp-edged pieces of shell without injury. They lose fluid and die after a while. Crumbled eggshells are also suitable for preventing snail damage. This method results in a slow death, similar to diatomaceous earth. Spreading eggshells offers benefits for the environment and other living beings.
- environmentally friendly method
- Leftovers are recycled
- Eggshells provide birds with a calcium-rich food source
Molasses
The tough substance prevents the caterpillars from moving to the base of the stem. The barrier effect is reinforced by sawdust and wheat bran, which are mixed with the molasses. If the pests try to crawl over the mass, it sticks to the body and makes further movement more difficult. The pests can be collected and disposed of to save them a slow death.
Tip:
Since the caterpillars dig holes, you should spread the thick mixture near the base of the stem. Draw circles around the plant.
Plant collar
Home-made collars that are placed in the substrate around each individual plant are suitable for plants in raised beds. For this you can use cans or plastic scraps that you cut accordingly. The collars should be about ten centimeters high so that the cutworm cannot climb over the obstacle. They are inserted about 2.5 centimeters deep into the substrate.
- easy to make
- cost-effective and ecological
- suitable for small beds with few plants
Targeted combat
If the pest infestation was not discovered in time, the population may have already expanded significantly. In this case, direct control of the caterpillars using lethal means helps.
corn semolina
The caterpillars like to eat the powder. In this way, the fine grains enter the digestive tract, where they cause damage. Large amounts of corn semolina lead to the death of the pests. Sprinkle the powder on the substrate. You should use the product carefully, as the sweet smell could attract other pests.
Diatomaceous earth
It consists of finely ground fossils and is an ecological variant because diatomaceous earth does not harm people, plants or other animals. The powder contains a glass-like quartz dust whose grains are very sharp-edged. They damage the outer skin of the cutworms, causing them to dehydrate and slowly die. The mealy dust settles on the surface of the pests. It destroys the lipid layer of the outer skin, which protects the caterpillars from fluid loss. The disadvantage of this method is that the caterpillars die very slowly and it can take a long time for an entire population to dry out.
- powdered agent for controlling cutworms
- can be spread at any time
- Rain washes away the powder
roundworms
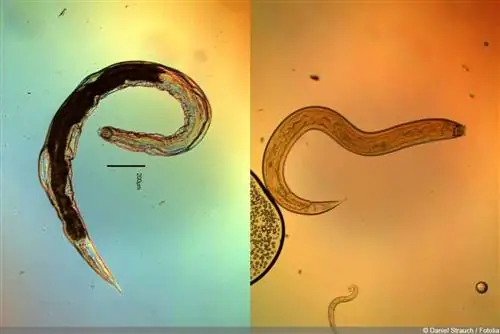
The beneficial insects known as nematodes live in the substrate. They reach a length of 0.6 millimeters and prove to be natural opponents of numerous larvae that live in the soil and on the substrate. The species Steinernema carpocapsae specializes in cutworms. They kill the caterpillars and feed on the tissue. In order for the nematodes to survive, the temperature in the soil must be above 14 degrees Celsius for a few hours. A drop in temperature at night does not harm the beneficial insects.
- Nematodes are available in powder form
- Powder is mixed with water and poured onto the substrate
- Beneficial insects can be used between May and September
Bacteria
Bacillus thuringiensis is one of the beneficial bacteria that kill cutworms. Since they do not destroy harmful species of moths and butterflies, the bacteria should be used with caution. They are applied directly to the substrate and can be used both as a targeted control and as a preventive measure. In order to permanently protect young plants from pest infestation, the products are used until the plants have developed strong stems.
- Bacteria is available as a pesticide
- Application in the afternoon
- apply again after rainfall
Prevention
The first feeding period ends with spring. In the coming months the butterflies will look for places to lay their eggs. Weeds and grasses, whose plant parts die off in autumn, offer optimal protection for eggs with their hollow stems. Removing wilted plants prevents egg laying. This measure also ensures that beneficial insects cannot find sheltered places. It is better to plant different types of plants so that an intact habitat is created. Useful animals such as toads, meadow larks and fireflies can spread in cultures with a great diversity of plants.






