- Author admin caroline@plants-knowledge.com.
- Public 2023-12-17 03:39.
- Last modified 2025-01-24 12:45.
If you want to build a property in this country, you will inevitably come across the floor area number (GRZ). This is a value for determining the permitted development area of the property. We will explain to you how to correctly calculate the floor area number.
Floor area number explained
According to Section 19 of the Building Use Ordinance (BauNVO), the floor area number (GRZ) is a decimal value that indicateswhat percentage of the area of the property you are allowed to build onThemaximum limit is usually 0.8 (exception: core areas), which corresponds to a value of 80 percent. The maximum value for the GRZ I is determined by the individual municipalities in the respective development plan for the neighborhood or area. The GRZ serves to maintain sufficient natural space on the property. Furthermore, she ensures that the building fits into the image of the community by not allowing the property to be built on too heavily.

GRZ I and II
The GRZ is divided into two categories, which together result in a maximum value of 0.8 in Germany:
- GRZ I (main facilities)
- GRZ II (auxiliary facilities)
The respective categories describe the elements and structures that belong to them. The main facilities include the primary house including the walls, terraces, balconies and basement exits. All other systems belong in GRZ II, such as:
- Garages (underground garages, outdoor garages)
- Pitches
- Garden houses
- Solar or PV systems
- Pools
- Playgrounds
- underground shafts
- Pits
- Tanks (e.g. oil or gas tanks)

When planning, pay close attention to how many ancillary systems you want to integrate. They lead to the buildable area being exceeded. This is only permitted by 50 percent until the GRZ reaches a maximum value of 0.8. At the same time, the ancillary facilities must not be directly connected to the main building. When planning, find out if an overage is possible. If not, a (usually costly!) dismantling can be arranged. For example, if the GRZ I of the property is 0.6, the GRZ II is only 0.2, otherwise the maximum value will be exceeded.
Note:
Unpaved paths on the property and roof overhangs are not covered by the GRZ. They can be implemented independently of the GRZ.
Determine floor area
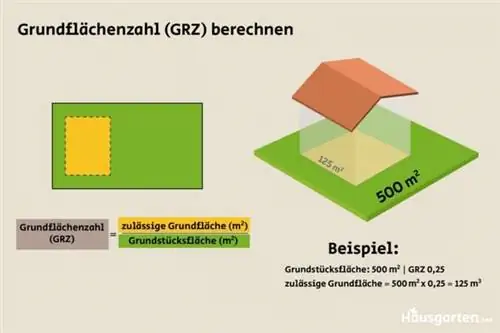
The floor area number specified in the development plan is used to calculate the floor area available to you. The permissible floor area depends not only on the GRZ, but also on the size of the property, as can be seen from the following formula:
Land area in m² x GRZ=buildable area
It helps with the determination because you only have to insert the individual values into the formula and calculate them. Use an example calculation to familiarize yourself with the calculation. For this we assume a property size of 500 square meters. On average, the size of the property in Germany is between 400 and 600 square meters. The GRZ is 0.25. This is often the case in small settlements, weekend houses or residential areas. In urban or industrial areas the value is usually significantly higher. To calculate the buildable area, we insert the values into the formula as follows:
500 m² x 0.25=125 m²
The buildable area of the entire property is therefore 125 square meters. These are available for development.
Calculate floor area number

You can also determine the GRZ yourself based on the available floor space. This is important if you want to check whether an existing building or design exceeds the GRZ specified in the development plan or not. In particular, structures in the GRZ II category that are subsequently connected to the main building can cause problems if the GRZ is exceeded. You can calculate the floor area number as follows:
buildable area in m² / land area in m²=GRZ
As with determining the floor area, enter the appropriate values into the formula. For clarity, we use the sizes from the previous calculation:
125 m² / 500 m²=0.25
As you can see, the buildable area corresponds to the GRZ. If the buildable area changes, this will of course affect the GRZ. Another example assumes a finished main building with a floor area of 180 square meters. The example calculation shows whether this still corresponds to the specified GRZ:
180 m² / 500 m²=0.36
The main building is too big in this case, which could lead to problems.
Note:
External stairs are always part of the floor area of the main building, which you must take into account when determining the GRZ.
Frequently asked questions
Who has to apply for a possible exceedance of the GRZ?
Primarily this is the construction planner. Ideally, the building planner is the actual architect, designer or the responsible construction office. This prevents problems with the application and only the exact elements for the possible excess are listed.
What is the difference between the GRZ and GFZ?
While the GRZ refers exclusively to the buildable land area, the floor area number (GFZ) specifies the maximum area the building floors may take up. This is also specified by the development plan. The factor for calculating the maximum floor area is also given as a decimal value and is usually between 0.5 and 1.0. It is not limited by the GRZ and is ideally divided over several floors.
How does the GRZ affect the property value?
The more building space is available, the more lucrative the property is. The reason for this is the available living and usable space. You can place a larger house, luxury elements such as a pool and even components for your own energy production. The available building space significantly increases the property value.






