- Author admin caroline@plants-knowledge.com.
- Public 2023-12-17 03:39.
- Last modified 2025-01-24 12:45.
Applying plasterboard is easy. Assembling the substructure is more complex because the safety and service life of the installed wall depend on it. We show here which distances need to be maintained.
Substructure
Plasterboard is not attached directly to the wall or ceiling. Instead, a base must first be constructed and fixed. This can be made of wood or metal. For walls, simple battens are sufficient. For ceilings, counter battens are also required to create the necessary support. The function of the construction under the Rigips elements is, on the one hand, to compensate for unevenness in the wall or ceiling and, on the other hand, to securely fix it. In addition, the space between the wall and the plasterboard can be used for additional insulation.
When designing the base, various factors must be taken into account. These include, among others:
- Distance between the horizontal and vertical depending on the dimensions of the plasterboards
- Observe manufacturer’s instructions
- can be made of wood or metal
- necessary load capacity depending on the panel weight
- choose stable beams or profiles
Note:
As a connecting element between the subsurface and the plasterboard, the substructure must withstand high loads. Therefore stability is crucial. For this reason, the type and distances within base elements depend primarily on the weight of the panels. The greater their thickness and the higher the weight, the smaller the distance between the beams or profiles must be.
Walls
Simple battens are completely sufficient for walls. It consists of two horizontal beams or profiles, between which vertical beams are inserted and fixed.
The distance depends on the properties of the plasterboard:
- Orientation
- Width
- Strength
For 125 centimeter wide panels, it is advisable to attach them to three beams to achieve the greatest possible stability. This can also make sense for 62.5 centimeter wide panels if a greater thickness and therefore a greater weight is chosen.
Tip:
For a wooden structure, beams with a width of at least four centimeters should be used. Six centimeters is more suitable. This creates a larger contact surface and therefore more space for screwing on the plasterboard.
Counter battens
The counter battens are based on the simple battens. However, it is expanded to include horizontal beams or profiles across the entire area. This creates a grid. It is used for ceilings.

The distances here again depend on the dimensions of the plates. However, it also decides whether wooden beams or metal profiles are used.
Metal profiles have a higher load capacity and a lower weight. Therefore they can be placed at greater intervals. The manufacturer's information is crucial here.
Distances on walls
Plasterboards are available in different dimensions. The standard width is:
- 60cm
- 62, 5 cm
- 125 cm
For 60 and 62.5 centimeters, the width can be used as a guide for the distances between the vertical bars. This corresponds exactly to the width of the panels. Starting from the wall, 60 or 62.5 centimeters are measured and marked on the horizontal beams. The verticals are cut so that they can be inserted exactly between the horizontals or, better yet, clamped. Insert and fix with screws at the marked points. The bars must be aligned so that the marking is exactly in the middle. In this way, there is enough wood overhang for both panels to be attached on the right and left for screwing.
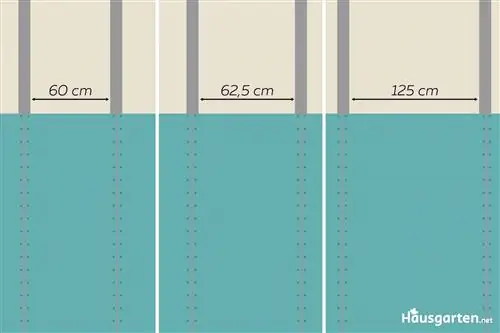
For very heavy versions or panels with a width of 125 centimeters, an additional fixation in the middle is recommended. Here, too, a vertical beam is inserted every 62.5 centimeters and the plate is screwed to the left, middle and right to the beam running underneath.
If dimensions deviate from the standard, please note that the plasterboard panels must be screwed to the substructure at the edges and, if necessary, along the middle.
Distances on ceilings
The grid-shaped construction is used as a basis on ceilings because it has a higher load-bearing capacity. For this purpose, the so-called basic battens are first attached. These are the beams or battens that are attached directly to the ceiling. The cross or support battens are screwed onto this base batten. These are transverse slats. They are used to attach the plasterboard panels.
With wooden beams, a distance of 50 centimeters between the individual elements should not be exceeded. This applies to both variants of the battens. Other values may apply to metal profiles. The manufacturer's information is crucial here.






