- Author admin caroline@plants-knowledge.com.
- Public 2023-12-17 03:39.
- Last modified 2025-06-01 06:48.
If you have decided on a raised pond, you will find numerous tips below to ensure that it works with clean water, great plants and impressive fish keeping.
Material and border
One of the most important criteria for self-construction is the selection of the material or the border. (Whiskey) barrels or other wooden materials are often used. However, it should be noted that wood is not weather-resistant and can stretch/deform. Without special impregnation and regular care, wood as a raised pond material does not retain its shape over the long term. If you want to save a lot of work in the long term, choose galvanized aluminum.
Size
Many people build the pond first and then think about which fish and plants they should put in it. This can have fatal consequences, because the size of the high pond must be adjusted so that the oxygen content in the water works and neither fish die nor a mud bath occurs. Therefore, always adjust the pond size based on the desired planting and fish population. Of course, the available space at the location also plays a role. If this does not provide more than what is needed to set up a small raised pond, fewer fish and plants are possible.
Stable ecosystem
High ponds are generally not to be viewed as a natural biotope with high ecological value. However, it can become one and remain stable if enough water can fit in it. A stable ecosystem can be achieved from 100 liters.
High Pond Depth
If fish are added to a pond, whether as a finished product, in the ground or as an above-ground specimen, the depth should be at least 80 centimeters. Depth means the height of the water. Only then can it be guaranteed that there is sufficient oxygen and freedom of movement for the fish. However, it depends on the specific type of fish.
Pond pump
If it is a mini raised pond, a pump is usually not necessary if the water depth does not exceed one meter and the water volume does not exceed 300 liters. However, it makes sense in any case if the following factors apply:
- Many small fish, which cause a lot of dirt and adversely affect the water quality
- To reduce algae formation when raised ponds get a lot of sun
- For winter storage to avoid complete freezing, especially if high ponds are in a northerly direction and/or in the shade
- High ponds with a water volume of 500 liters or more and fish always require a circulation pump for oxygen enrichment
Location
The best and fanciest raised pond will bring little joy in the long term if it is installed in a suboptimal location. Use the following tips for the ideal location to avoid problems intelligently:
- Light: five/six hours of sunlight are ideal to prevent algae formation and the spread of pathogens
- Away from deciduous trees because leaf litter acts like fertilizer on the water
- Secured location so that neither your own children nor neighbors' children can reach it unnoticed
- If necessary, easily accessible power source if electrical devices need to be connected for cleaning, filtering or circulation
Underground
In order to achieve a balanced, even water pressure in the pond, it is important to ensure that the surface is level. As soon as it has only minimal unevenness, the waterline changes. This leads to higher water pressure in one place or another. As a result, the weight shifts, which in the worst case scenario makes it possible for it to tip over. Slight unevenness can be easily leveled out with play or building sand.
Tightness
When building and setting up your own high pond, long-term waterproofness can be achieved with the following tips:
- Use pond liner especially with wooden material, as wood “works” and can warp and become leaky
- Be sure to clear the floor of stones and root residues before setting up
- Fleece on the substrate prevents displacement by weeds and/or roots deep in the ground
- If necessary, work a close-meshed grid into the soil to prevent earth animals from eating through it (e.g. voles)
Pond Liner
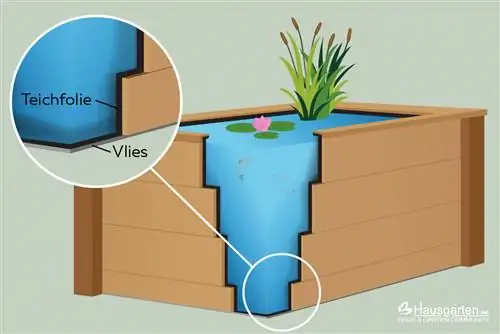
Pond liners are offered in a wide variety of thicknesses and qualities. Those who rely on cheap prices often pay for this with repeated purchases and more work due to the need for replacement as quickly as possible. A pond liner is exposed to constant stress due to the water pressure, the plants, the fish and also the temperatures. In order to maximize the longevity of a pond liner, you should pay attention to the following properties when purchasing:
- Weather and UV resistance as well as frost resistance
- Thickness of at least 0.5 millimeters
- Material: non-toxic polyethylene
- High-quality workmanship and quality
Planting
Without plants, a pond not only looks half-finished and boring, but the water quality also suffers. If you want to build your own raised pond and plant it with plants, you should take the following tips to heart:
Create floors
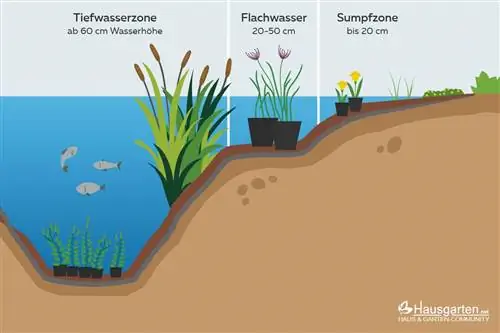
In order to prevent the plants from slipping and to create a higher water purification power through plants, it is important to create tiers. The floors are set to specific heights like steps:
- First floor: Swamp zone up to a maximum water height of 20 centimeters
- Second floor: Shallow water zone between 20 and 50 centimeters water height
- Third floor: the bottom as a deep water zone from 60 centimeters
- In shallower raised ponds, the shallow water zone is the bottom - the third floor is omitted
- No fourth floor required for raised ponds with a water depth of more than 120°
Water quality
Simply attach the water hose and fill the raised pond - this is the most common procedure for filling ponds with water. Later, many people wonder why plants don't grow, develop poorly or even die. This may be due to the tap water if it contains lime. Many plants cannot tolerate lime. Therefore: it is better to use rainwater for filling. This also saves the effort of subsequent descaling.
Let water rest
When building raised ponds, the pond water should be allowed to rest after completion - especially if planting with oxygen plants is planned. The “fresh” water still has a few microorganisms and the CO2 content is correspondingly low. As a result, the new aquatic plants have difficulty growing and/or growing. A rest period of four weeks is ideal. If immediate planting is desired, the water should be prepared with so-called CO2 tabs. These are available online, in well-stocked hardware stores and garden centers.
Plant choice
The choice of plants should be made carefully and well planned if you are planting it yourself. There are numerous aquatic plants, but not all of them like being in low or high water equally. Some also need more sun than others. It is also important to consider whether the specimens are hardy or sensitive to cold. The following are a few examples of aquatic plants with different requirements and properties:
Water lettuce (Pistia stratiodes)
- Growth: rosette-like, free-floating
- Growth width: 20 to 30 centimeters
- Growth height: ten to 15 centimeters
- Flowers: white, from June to July
- Location: Sun
- Hardy: no
- Suitable for small and large raised ponds, swamp zone
Water lily 'Hermine' (Nymphaea x cultorum 'Hermine')
- Growth: rhizomatous, strong-growing
- Growth width: 100 to 150 centimeters
- Growth height: five to 15 centimeters
- Flowers: white, from May to July
- Location: Sun
- Hardy: up to 23.4 degrees Celsius (hardiness zone 6)
- For medium to large raised ponds in deep water zones
Dwarf Cattail (Typha minima)
- Growth: tightly upright, forming runners
- Growth width: 30 to 40 centimeters
- Growth height: 40 to 60 centimeters
- Flowers: single, brown, from June to July
- Location: Sun
- Hardy: up to 23.4 degrees Celsius (hardiness zone 6)
- Ideal for small and large raised ponds, location in a water depth of 20 centimeters (swamp zone)
Water Filtering Plants
The following are some examples of planting specimens that are among the best water-filtering oxygen plants:
- Water buttercup (Ranunculus aquatilis) - highest filter power in spring and winter
- Hornleaf (Ceratophyllum demersum) - highest filter power in summer and autumn
- Lawwort (Potamogeton natans) - highest filter power from spring to late summer
- Water pest (Elodea) - highest filter power from summer to late autumn
- Fir fronds (Hippuris vulgaris) - highest filter power from spring to late summer
Tip:
Since not every “filter plant” releases oxygen all year round and is therefore not effective against algae formation, it is recommended to pay attention to variety and different variations in the aquatic plant species.
Stones for earth surface
Unnecessary contamination should be prevented by placing stones on the soil surface of the plant baskets after planting. These hold the earth down so that it doesn't wash out and fish don't disturb it. It is important that these are rounded stones without sharp segments so that they do not damage the film if they fall out.






